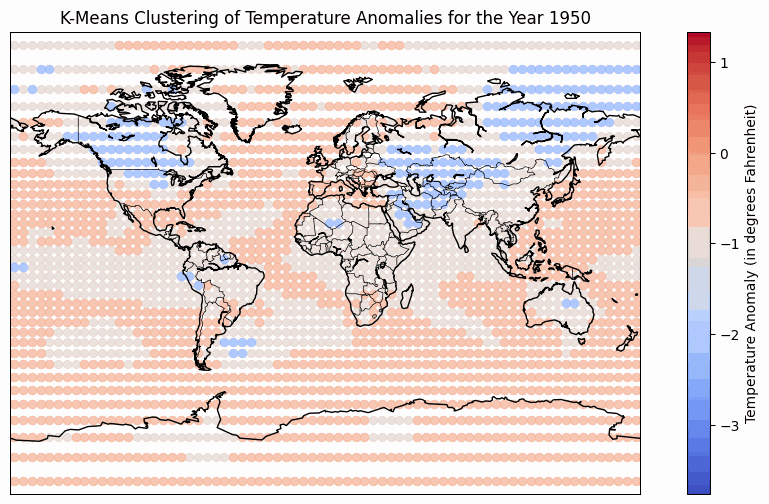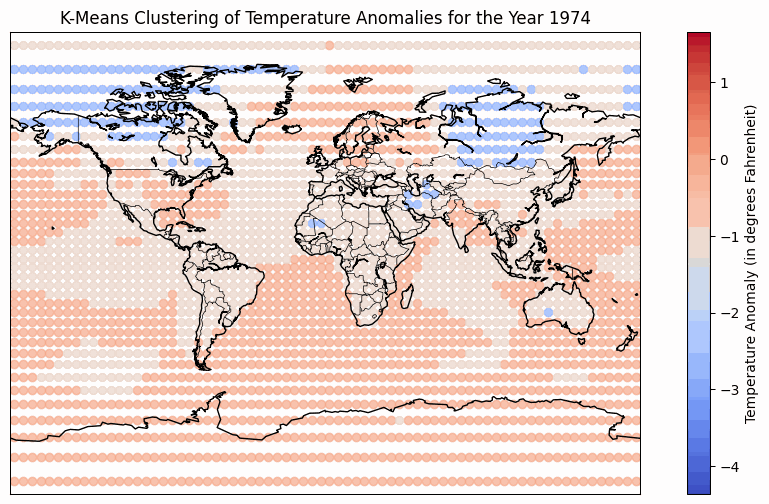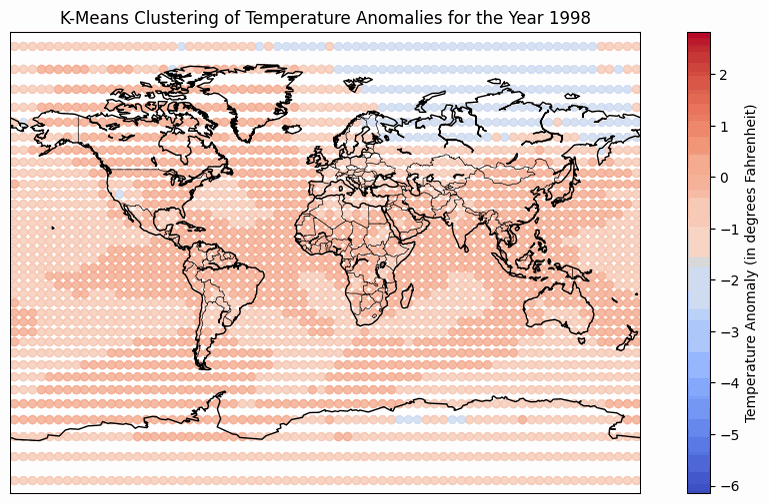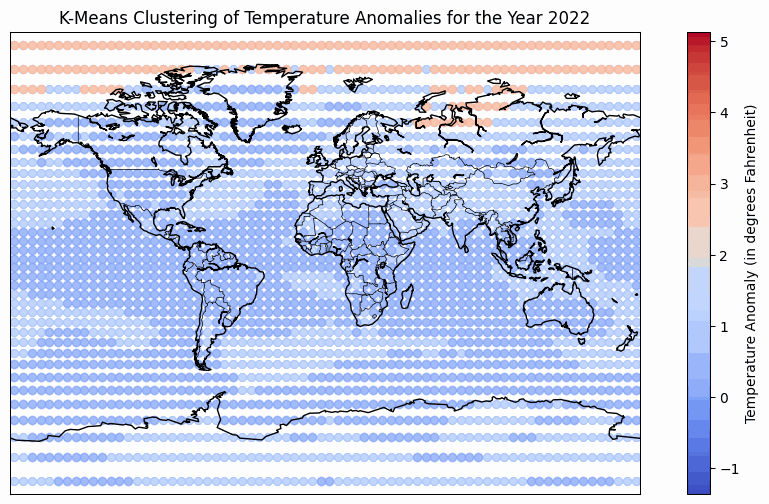
Temperature Anomaly over period of time from 1950 - 2022
The temperature anomaly heatmap has a refined colormap that uses blues for temperatures below the baseline and reds for temperatures above the baseline. This makes it easier to understand as red signifies heat and blue is associated with cold. The color binning technique is used to categorize temperature anomalies into distinct ranges for better visualization. The darker blue color represents temperature anomalies from -2℃ to -4℃, while lighter blues represent anomalies from -2℃ to 0℃. Similarly, a darker red represents anomalies from 4℃ to 2℃, and lighter reds represent anomalies from 0℃ to 2℃. Notably, the use of color saturation signifies higher anomalies, while color hue indicates the direction of the anomaly (positive or negative). The implementation of a video-style animation addresses the challenge of showcasing temporal variations on a static map. Interactive controls, including a play button, speed adjustment, and a year slider, empower users to customize their viewing experience. The play button facilitates the observation of temperature anomaly trends across multiple years, while the speed adjustment allows for a quick overview or a more detailed analysis. The year slider enables users to navigate to specific years, control the pace of the animation, and track their progress. Additionally, radio buttons offer playback modes such as "Once," "Loop," and "Reflect," allowing users to tailor the viewing experience to their preferences. However, a notable tradeoff of the video-style animation is the absence of hover, zoom, or pan functionality for the map. This limitation restricts users from analyzing specific areas or determining precise temperature anomalies at a given time, emphasizing a focus on overall trends in more general geographic regions.